Posted by Managementguru in E Sale Point
on Jul 17th, 2014 | 0 comments

I thought it would be helpful to create resource pages on some of the wonderful ‘Online Courses’ available. I recommend bookmarking these pages for your reference and convenience. Enjoy! Since our niche pertains to MANAGEMENT & BUSINESS ADMINISTRATION, let me start with a list of courses on Human Resources, the indispensable organizational factor. Learn how to recruit, hire, train and manage Human Capital. Human Resource Outsourcing ( HRO) has become necessary TO NOT ONLY HIRE BEST TALENT but also to RETAIN THEM. Human Resource Management Courses Let me first list some courses on HUMAN RESOURCE CERIFICATE COURSES 👈 Follow this link These courses include, PMP certification exam prep Payroll management Vendor relations Scrum master certification Employment regulations and programs These courses give you the ease of learning from the comfort of your home at very reasonable prices and also give you an opportunity for passive income by publishing video lectures on Udemy. If you happen to be very successful, this platform might become your main source of income, since people are always hungry for more information and knowledge. Don’t Miss Out On This Course HR Analytics using MS Excel for Human Resource Management Use Excel for HR Analytics, calculate HR metrics, build HR dashboards & ML models for Human Resource & People Analytics To Choose from over 210,000 online video courses with new additions published every month 👈 Follow this link Hope you enjoyed this post, and come back with your valuable feedback if you were benefited by enrolling in any one of these courses. Online learning has become the ‘ORDER OF THE DAY‘ and lot of universities and educational institutions are digitizing their teaching approach and if you happen to be an expert in your niche, ‘YOU ARE MOST WANTED‘. Disclosure: Please note that some are affiliate links, and at no additional cost to you, I will earn a commission if you decide to make a purchase. Please understand that I have experience with all of these companies, and I recommend them because they are helpful and useful, not because of the small commissions I make if you decide to buy...

Posted by Managementguru in Financial Accounting, Management Accounting, Principles of Management
on Mar 27th, 2014 | 0 comments

Management Vs. Financial Accounting Management Accounting : The process of preparing management reports and accounts that provides accurate and timely financial and statistical information to the management Financial Accounting : The purpose of accounting is to provide the information that is needed for sound economic decision making concerned with classifying, measuring and recording the transactions of a business. What is Management Accounting: Management accounting is the updated version of what you call financial accounting and the most circulated term in corporate business arena. Management involves planning, organizing, staffing, leading and controlling the resources available in an organization, namely the physical and human resources. Much importance is given to personnel management as they are the priceless assets of any organisation.But it is equally important for a firm to record all its business transactions for future reference and tax audits. Thus the necessity of accounting comes into the fray. Financial Statements Made Easy Functional Difference: Well, accounting means something to do with finance. So, what is the big difference, if it is financial or management accounting? One difference is in the title, and the other in their function. The rationale behind financial accounting is statutory, done for the benefit of shareholders, customers, government regulatory agencies, other external agencies, potential investors and the like. It records all business transactions that are purely monetary in nature and no further analysis is done. Essential for Management Planning: Management accounting is voluntary and reports are prepared to meet the internal needs of management. We talked about planning, for which interpretation and analysis of such quantitative data and other inputs becomes necessary to plan for future needs of management. The main functions being attention direction and problem solving, management accounting is primarily concerned with providing information relating to the various aspects of a business, like cost or profit associated with some portions of business operations. It employs techniques such as standard costing, budgeting, marginal costing, break- even analysis and so on., Inputs also stem from industry data, competitor data, published reports by public and private agencies and research studies findings, thus widening its scope for improvement in business operations. Financial Accounting: Financial accounting is restricted to deal only with “generally accepted accounting principles” and any deviation is considered to be errors for correction. Though it provides valid and authentic information, it lacks timeliness. The former restricts the accountant to a mere book-keeper while the latter transcends the role of the accountant to that of total business information technologist. Here he becomes an evaluator of different functional areas like marketing, production, purchase and personnel. As modern business is huge in size, complex, diversified and decentralized in terms of operations, financial accounting just does not fill the bill, as information is required as when an event happens at various hierarchical levels of an organisation. This infographic from Goodaccountants.com details the industries that employ the most accountants and auditors, and the results are very interesting! Management accounting is inter disciplinary in character and derives inspiration from organizational theory, economics, behavioral sciences, statistics and management. Although the paraphernalia required for management reporting is complex and expensive, it is worth the try, as it tries to compare and contrast the actuals with the standards and bring out variances if any. This is quite useful in determining the cost-effectiveness of a particular project or to be prepared for suitable action. Management accounting is nothing but a management information system where the managers have to be techno-savvy in order to handle the total information resource and project it suitably to the management to take timely actions for the increase in growth, profit and sustainability of the...

Posted by Managementguru in Business Management, Human Resource, Organisational behaviour, Principles of Management
on Mar 13th, 2014 | 0 comments
Operative Functions of HRM Staffing Staffing is one of the managerial functions. But this function is normally performed by the HR managers for all the departments of the firm. In most organizations, the HR department establishes personnel policies and coordinates the HR functions of all the departments. This function is also called the operative function or HRM function. It includes, amongst others, the processes of hiring, training, compensating, appraising and retaining employees, and attending to their labour relations, health and safety, and equality concerns. Procurement Procurement refers to a string of activities undertaken by the HR managers for filling the present and future vacancies of the organization. The activities include job analysis and designing, HR planning, recruitment and, finally, the selection of suitable employees. Here, job analysis refers to both the determination of specific tasks and responsibilities connected to a job and identifying the skills, knowledge and abilities required for the job holder. HR planning involves choosing and placing the right person at the right job and at the right time. Recruitment involves gathering a pool of applicants from which suitable employees may be selected. Lastly, selection involves screening, testing, interviewing and hiring the most suitable employees for the organization. SCOPE AND CHARACTERISTICS OF HRM Development Development here refers to both employees’ training and management development. HR managers are accountable for conducting and supervising training and development programmes for employees. The very purpose of a training and development programme is to increase the employees’ competencies in their job by improving their knowledge, skills and abilities. Training and development is widely accepted as a method for enhancing the employee skills, increasing the individual and organizational performance, improving the employee morale, and achieving the business growth and success. Compensation Compensation refers to the determination of the pay scale and other benefits for the employees. Establishing and maintaining the pay system of an organization is one of the principal jobs of the HR managers. They must devise ways to ensure fair and equitable pay rates. In addition, HR managers should regularly manage the performance evaluation system of the organization, and continuously design reward systems such as performance-linked incentive plans and bonus and flexible work schedules. Maintenance The maintenance function aims at retaining efficient and experienced employees in the organization. This calls for creativeHR practices. In this regard, HR managers are responsible for offering a wide range of HR programmes covering occupational safety, health promotion and physical fitness, canteen facilities, recreation activities, transportation programmes, employee suggestion schemes, career counselling and growth for creating a positive work environment. OBJECTIVES AND FUNCTIONS OF HRM Integration It consists mainly of industrial relations and aims at ensuring good relations between the management and the employees. HR managers have to implement industrial relations programmes that would ensure ethical and fair treatment in disciplinary action, grievance redressal, and career management processes. They should also counsel the employees and the management to prevent and, when necessary, resolve disputes over labour agreements or other labour relation issues. It is to be understood here that the functions of HRM can vary widely from one organization to another, depending upon its nature, size, and objectives. For instance, a smaller organization may follow a shorter HRM process with a greater emphasis on functions like procurement and compensation and little or no priority for activities like training and development and industrial relations maintenance. On the contrary, large organizations may pursue a longer and more comprehensive HRM process to meet the requirements of both the management and the workforce. WANNA TAKE A HR QUIZ N CHECK YOUR HR IQ? 1. The development and application of employees’ skills and energies to accomplish the goals and objectives of the...

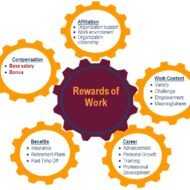
Posted by Managementguru in Business Management, Human Resource, Principles of Management
on Mar 2nd, 2014 | 0 comments
Objectives and Functions of HRM Human Resource Management is very challenging because of the dynamic nature of the people and it is not only managing men but involves administering a social system. According to Dale Yoder “Man power management is the function or activity in directing working men and women in maximizing their satisfaction in employment.” George R. Terry says, “Personnel management is concerned with the obtaining and maintaining of a satisfactory and satisfied work force.” OBJECTIVES OF HUMAN RESOURCE MANAGEMENT: 1. Social Objectives: a) Facing the challenge of unemployment and providing people with maximum employment opportunities is the first and foremost priority of countries like India where there is pressure of population growth. b) The employees must be able to derive maximum satisfaction from the work performed. c) The system should facilitate harmony and co-operative endeavor for one and all. 2. Personal Objectives: Job satisfaction and rewards in the form of pay, promotion and recognition is aimed at, on the part of employees. This can be achieved by providing adequate remuneration, opportunities for advancement, facilities for training and development, job security and proper work. 3. Enterprise Objectives: This can be achieved by selecting the right people for the right job, empowering them through training, development and participation. FUNCTIONS OF HUMAN RESOURCE MANAGEMENT: 1. Planning: Assessment of future man power requirement is done with the help of man power inventory chart followed by the recruitment and selection process. A clean job description is needed to lure people with the right skills for the right position. It is the responsibility of the manager of a firm to lay down specifications of the qualities and skills required by the workers and determining sources from where the workers are to be recruited. Selection is done by means of written test and personal interviews. 2. Organizing: This involves proper designing of organizational structure, the inter relationship between jobs, establishing smooth channels of communication, assignment of authority, responsibility and creating accountability, establishing line and staff relationship etc. 3. Directing: Issuing orders and instructions down the line and motivating the work force to carry out those instructions satisfactorily. Positive motivation in the form of financial and non-financial incentives, a good working environment is essential on the part of the management. 4. Controlling: The motive is to ensure that performance of each worker coincides with the plans or standards. Bench marking, Total quality management and Six sigma are some of the popular concepts of standardization. → Scope and Characteristics of...

Posted by Admin in Accounting, Management Accounting
on Jan 29th, 2014 | 0 comments

Management accounting combines accounting, finance and management with the leading edge techniques needed to drive successful businesses. The process of preparing management reports and accounts that provide accurate and timely financial and statistical information required by managers to make day-to-day and short-term decisions










