Posted by Managementguru in Human Resource, Organisational behaviour, Training & Development
on Jul 28th, 2014 | 0 comments

Anger Management What is Anger? To put in a layman’s perspective, When something doesn’t happen the way we want it to When somebody tries to dominate us When we are forced to do something When we get disappointed if things are not favorable and many more situations that kindle within us a feeling – which is called frustration if the intensity is mild and rage if the intensity is huge. This type of anger pertains to “self”; anger also erupts if our loved ones, near and dear ones experience threat or when you want to oppose a social stigma or when you feel helpless in a situation.” On top of all this “A Hungry Man is always Angry“, Do you agree with me? I want to ask a simple question, “Are the poor to blame for being poor?“. Well, this is a social problem and every one of us must be angry if the people of our own country are below the poverty line and not being able to eat atleast twice a day. How do we define Anger Management? Coming to Anger Management, it is training for temper control and is the skill of remaining calm. It has been described as deploying anger successfully. Anger management is the process of learning to recognize signs that you’re becoming angry, and taking action to calm down and deal with the situation in a positive way. We have to understand the crucial fact that ” In no way does anger management mean holding the anger in or trying to keep from feeling anger. Anger is a normal human emotion, a healthy one when it is expressed appropriately“. What Makes People Angry? I want to list down some of the most common things that make people angry. The most common factors that make people angry are: Grief – losing a loved one. Sexual frustration Rudeness Tiredness Hunger Pain Withdrawal from drugs or some medications Some physical conditions, such as pre-menstrual syndrome Physical illness Mental illness Alcohol, some drugs, alcohol abuse, drug abuse Injustice Being teased or bullied Humiliation Embarrassment Deadlines Traffic jams Disappointment Sloppy service Failure Infidelity Burglary Financial problems Being told you have a serious illness Courtesy – http://www.medicalnewstoday.com/ You know, I get angry even if I hear somebody munching or chewing something and I can never stand that sound! I googled to know more about my shortcoming and was relieved to find that I have good company on this issue. Read this news: ‘The sound of my boyfriend chewing makes me want to strangle him’: Model, 20, has a phobia of NOISE which makes her fly into a rage when she hears someone eating.” (This medical condition is called “Misophonia” which literally means hatred of sound and seems to be a neurological disorder). Faith Watson, 20, has misophonia – the hatred of sound Certain noises – including chewing – make her irrationally angry At meals she has to have the TV on so she can’t hear people chewing She had to drop out of college after being tormented by classroom noises Now she has been officially diagnosed, she is rebuilding her life and trying to make a career as a model Courtesy – http://www.dailymail.co.uk/health/ I personally feel that people have become restless in general and want everything to happen in a jiffy. Rationale and Logic have taken a back seat and we all are evolving as one group with SUPER-EGO and IMPATIENCE. What is the reason behind this? Are we becoming insensitive to others’ feelings? Have we forgotten to enjoy moments of happiness how small it may be? In my opinion there are only two types of anger: Constuctive Anger – that which helps to...

Posted by Managementguru in Business Management, Marketing, Organisational behaviour, Principles of Management, Strategy
on Mar 22nd, 2014 | 0 comments
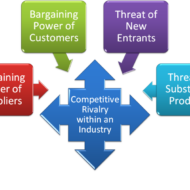
PORTER’S FIVE FORCES Porter’s five forces analysis-draws upon industrial organization (IO) economics to derive five forces that determine the competitive intensity and therefore attractiveness of a market. Survival of the Fittest: True to Darwin’s theory “Survival of the fittest”, only competitive firms survive in the business market, provided, they have made the right strategic choice by comprehensively analyzing their position in the industry. Every organization is part of the industry and almost all of them face competition. Thus, industry and competition are the vital considerations for making a strategic choice. All the firms in a particular industry vie for the same set of customers by offering identical or similar products with minor variations. The analysis of the external environment in relation to the context of industry attractiveness thus becomes essential. A Critical Evaluation of Michael Porter’s Five Forces Framework Industrial Analysis: Industry analysis helps a firm to also fix long range plans, by gauging long term growth opportunities present if any. Strategic choice is nothing but, to screen all possible strategic alternatives followed by narrowing down the choice to the best suited and feasible alternatives and ultimately choosing an optimum strategy. To explain it in more clear terms, let us look at this example. Say, if there are three big players of car manufacturers in an automobile industry. Each follows their own strategic style to capture the market. What are the threat factors? Threat can be in the form of four-wheeler manufacturers like trucks and jeeps, but these cannot be competitively priced. Threat can be in the form of suppliers who dominate the industry by having a grip on the supply of components, sub-assemblies and accessories. Threat in the form of new entrants, but the growth might be restricted due to government regulations. A thorough analysis of the automobile industry thus made can make things clear to the firm, as to where they stand in terms of market share, what are their strengths and weaknesses, who pose a threat, what are the potential opportunities for growth and to tap market segments whose needs are unidentified. Still, it will be a seller’s market where the buyers have no bargaining power. On the other hand, if the weather does not favor its growth, the firm has to immediately decide on its next course of action, calling for diversification. The possible threats for a firm can come from five directions as mentioned below: Potential threat from new firms entering the market Threat from substitutes available in the market Threat from competitors Bargaining power of the suppliers Bargaining power of the buyers The structure and dynamics of an industry has to be analyzed in order to determine the intensity of competition and profitability. As the market is very dynamic, it becomes mandatory for firms to evolve strategies embracing a modern approach, with emphasis on reappraisal of existing strategy in the light of changing external conditions and formulation of alternative...

Posted by Managementguru in Business Management, Change management, Marketing, Organisational behaviour, Strategy
on Feb 18th, 2014 | 0 comments

SWOT and Synergy SWOT Analysis On the basis of its resources and behavior, an organization develops certain strengths and weaknesses which when combined lead to synergistic effects. Such effects manifest themselves in the form of organizational competencies. It is necessary for a firm to look for and develop factors that adds to its strength, as strength is considered to be an inherent capacity which an organization can use to gain strategic advantage. Pic Courtesy: Clickfunnels A weakness, on the other hand, is an inherent limitation or constraint which creates a strategic disadvantage for the organization. Financial strength, for example, is a result of availability of financial sources and efficient rotation of funds. A weakness in the operations management area might be a result of inappropriate plant location, obsolete plant layout and technology. It has to be noted that an organization cannot enjoy the privilege of having only strengths and devoid of any weaknesses. Then the performance level would become saturated to the point of monotony and there exists no scope for growth or improvement. Only when presented with challenges, any functional area exhibits synergy, as strengths and weaknesses do not exist in isolation but combine within a functional area, and also across different functional areas. Synergy Synergy is needed at all levels for better productivity. Say, within a functional area like marketing, synergistic effort may occur when the product, pricing, distribution and promotional aspect support each other, resulting in higher level of marketing synergy. The same when happens at an even higher level, leads to operating synergy, say, for example, synergistic efforts between marketing and production department to decide on the production forecast and pricing. Distinctive competence helps a firm to develop strategic advantage that leads to comprehensive growth and development. Limitations of SWOT: A SWOT analysis can over emphasize internal strengths and overlook external threats It can be static and may ignore the changing circumstances It might give undue importance to a single strength or an element of strategy A strength is not necessarily a source of strategic advantage. Amazon.in...






