Posted in Accounting, Financial Accounting, Management Accounting
on Feb 14th, 2014 | 0 comments
Ratio Analysis – An Introduction
What is Ratio?
The relationship between two variables expressed mathematically is called a ratio.
It refers to the systematic use of ratios to interpret the financial statements in terms of operating performance and financial position of a firm.
Some important definitions:
- “The relation of one amount, a to another b, expressed as the ratio of a to b”– Kohler
- “Ratio is the relationship or proportion that one amount bears to another, the first number being the numerator and the later denominator” – H.G.Guthmann

Significance of ratio analysis:
- It consolidates and simplifies the accounting information or data
- It is a clear indicator of an organisation’s efficiency
- It helps in the evaluation of a firm’s performance by comparing the past and present ratio
- It aids the management in formulating poilicies, preparing budgets etc.,
- It points out the liquidity position thereby assisting in assessing the short-term obligations and long-term solvency
- It facilitates inter-firm and intra-firm comparison, the former to understand the position of firm in the market and latter to gauge the performance of different divisions of the firm.
- Since ratios have the power to speak, they are considered as effective means of communication
A broad classification of ratios:
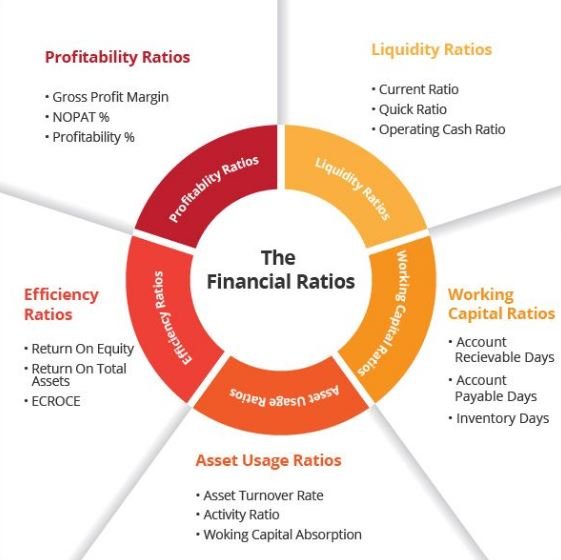
Pic Courtesy : Financial Ratios
CLASSIFICATION BY FUNCTION
1. Solvency
Short-term Long-term
Current ratio Proprietory ratio
Liquid ratio Debt-Equity ratio
2. Profitability
- Gross profit ratio
- Net profit ratio
- Operating profit ratio
- Return on Investment ratio
3. Activity ratio
- Fixed assets turnover ratio
- Debitors turnover ratio
- Creditors turnover ratio
- Stock turnover ratio
4. Leverage
- Financial leverage ratio
- Operating leverage ratio
- Capital gearing ratio
CLASSIFICATION BY STATEMENTS
1. Balance sheet ratios
- Current ratio
- Liquid ratio
- Proprietory ratio
- Debt-Equity ratio
- Capital Gearing ratio
2. Profit and Loss Account ratios or Profitability ratios
- Gross profit ratio
- Net profit ratio
- Operating profit ratio
- Return on Investment ratio
3. Inter-Statement ratios or Turn-over ratios
- Fixed assets turnover ratio
- Debitors turnover ratio
- Creditors turnover ratio
- Stock turnover ratio