Posted by Managementguru in Change management, How To, Human Resource, Learning, Organisational behaviour, Productivity, Strategy, Training & Development
on Jan 19th, 2022 | 0 comments
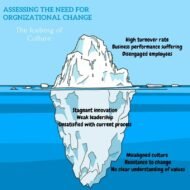
Today’s leaders around the world cite culture and employee engagement as one of their top organizational challenges. They are in a position to identify and assess the need for change in their organizations as certain issues are only evident like a tip of the iceberg. In order to kick start organizational change management, leaders can do these two things. Constantly Ask Why? Why do we do it this way! If “That’s the way we’ve done it always” is the answer, it’s time to delve deep into underlying issues that are waiting to be addressed.Consult an expert from outside and allow them to experience your firm for a while. They might be able to bring out the existing flaws. New perspectives always end in benefits. Organizational Change Management Factors contributing to failure: Management behavior does not support changeEmployees’ resistant to changeInadequate resources / budgetOther obstacles Organizational culture eats organizational change for breakfast, lunch and dinner- so, don’t leave it unattended. Mind-set Shifts for Organizational Transformation From profit to purposeFrom hierarchies to networksFrom controlling to empoweringFrom planning to experimentationFrom privacy to transparency The transformation journey can’t rely only upon technology innovations as innovations are a result of in-depth factors including mind-set, behavioral constructs, leadership and culture. The most profound business challenge we face today is how to build organizations that can change as fast as change itself. – Gary Hamel An Employee always tend to think and fear “My boss does not like me!” This mentality stops him/her from expressing his/her thoughts freely. This is a definite do-harm factor for the firm as suggestions from employees are valuable as they stem from their work experiences. Be it inter personal or even judgemental, an employee must be given a free hand to sincerely express his point of view. Culture defies strategy The key is to make your employees happy. Happy employees perform better. To make them happy, you just have to do one important thing as a leader. Listen. Listen. Listen. You can be straight forward, treat them like friends in order to create a great atmosphere. By doing this you are extracting their potential with ease. They come forward with excellent suggestions for the good of the company. Employee experience is all about emotional connect. References. Mindset Shifts For Organizational TransformationCulture and...

Posted by Managementguru in Business Management, Entrepreneurship, Human Resource, Leadership, Principles of Management, Training & Development
on Mar 18th, 2014 | 0 comments
Executive Development – Options are Wide Open Who is an Executive: A person or group having administrative or managerial authority in an organization. While “executive” and “manager” and “leader” are often used interchangeably, “executive” is commonly used to signify the top 5% to 10% of the organization. Executive Development : aimed at developing the skills and competencies of those that (will) have executive positions in organisation. Capabilities of a Good Manager: A good manager can make an organization grow, survive and shine amidst tough competition, if he is bestowed with corporate competencies such as perseverance, capacity to put in hard work, sense of loyalty and responsibility, all of which may be inherited or acquired qualities. Loyalty stems from internalized morality that may be a result of his value system. Executive success is what the organizations should aim for, and firms should try to figure out the fundamental components that make up the success formula or equation. Road to Self-Development: In less developed countries, employees are more than satisfied if they are provided with a job that offers safety and security. Their thinking is restricted to mere physical and biological comforts and does not go beyond that point, where self development and self-actualization come into the picture. In developed countries, the situation is quite different, where the workers aim for empowerment and look for reasons that motivate them to do a job. Money also has its due role to play, and people whose wages are very meager cannot be expected to aim for empowerment, where their single motive is mere survival. Abraham Maslow’s Point of View: Abraham Maslow puts forward the hierarchical needs theory, arguing that, there are five levels of needs for people in general, right from physiological needs at the bottom of the pyramid and need for self actualization at the top, and safety, security and esteem needs coming in between. He points out that, once a need is satisfied, it ceases to be a motivator. This is so evident in our day to day lives, where wants and needs never cease to exist and once a want is satisfied, human mind wanders to catch hold of another. So, organizations should understand and analyze, what factors best motivate their employees, particularly their managers (who might serve as a source of inspiration to their subordinates).It should be remembered that non-availability of jobs leads to dissatisfaction whereas availability of jobs need not motivate employees. Some factors which have been proven to be real motivators are as following: Recognition Opportunities for self development Additional responsibilities(lateral expansion) Timely rewards(in terms of money and appreciation) Security Inculcating a sense of belongingness Conducive corporate atmosphere Corporate culture Good human relations Economic burden makes people less enthusiastic and anxious in developing countries and this hinders them from delivering to their fullest potential. Also the bureaucratic approach followed by conservative firms, autocratic leadership style and lack of supportive atmosphere make people work like automatons devoid of creativity. Such firms may show good results in terms of productivity initially, but in due course has to pay the price, in terms of absenteeism, high attrition rates and less efficiency. It has been proven that job satisfaction is directly proportional to efficiency. When people find a job tedious and monotonous, they tend to lose interest, which will be evident from their lack lustrous performance. Performance management has its bearing on executive success and by providing with ample scope for career advancement and autonomy; managers prove their mettle even within limited scope of resources. Acceleration of executive change implies the development of the executive mind for performing managerial activities in a better way. Note : A survey of CEOs in Fortune 500 enterprises indicated that executives spend little time with their...

Posted by Managementguru in Business Ethics, Business Management, Entrepreneurship, Organisational behaviour, Principles of Management
on Mar 15th, 2014 | 0 comments
The Origin of Unethical Behavior Ethical considerations in business are important to managers as it is to individuals in their personal lives. Personal life and business life cannot be perfectly separated with respect to moral judgements. A number of factors have been established as significant in making ethical standards a primary concern of business managers. What are Values? For the individual, the job is the centre of life, and its value must be, in harmony with the rest of life, if he is to be a whole and healthy personality. In an industrial society. The values tend to become those of the entire corporate culture. The public is insisting that business leaders are, in fact, responsible for the general social welfare and that the manager’s responsibilities go far beyond those of running the business. Even if the manager insists on a narrow definition of his role as possible, it is, however, essential that he takes these intangibles into consideration since they are the real motivating force in an organization. Expectations of the Society: If an organization did not behave in accordance with the social systems and expectations, it may not merely lose its market share but face another piece of legislated control and might also lose its very right to exist. Many a times managers may be forced to compromise their personal ethics and moral values in order to achieve organizational goals. Everyday ethical decisions are usually made between the lesser of the two evils rather than obvious right and wrong. Often it may be difficult for the manager to free himself from taking a biased attitude and look at issues objectively. In spite of good intentions, he becomes involved in the situation and it becomes difficult to retreat and take a detached point of view in examining the issue from an ethical standpoint. In the light of these problems, certain examples can be cited to answer the question as to what constitutes unethical behavior. Padding expense accounts to obtain reimbursement for questionable business expense. Revealing confidential information of trade secrets. Giving or accepting gifts or favors. Using company property and/or materials for personal use. Leaving the job without abiding by the sales contract. Being severely critical of competitors. Attempting to corner opportunities by bribing public officials. Price discrimination, unfair trade practices, unfair pricing etc. , Dishonesty in fulfilling contracts. Politics inside the organization. Unless and until the professional manager puts the interest of the organization in front of his own, places the duty to the society above his duty to the organization wholeheartedly, there is no point in talking about ethics in theory. Though a number of firms spend their time, money and energy in formulating statements, in reality their enthusiasm is lost in practice. The gap between the espoused and practiced values creates a dissonance in the minds of the people, and as a result in the...

Posted by Managementguru in Business Ethics, Business Management, CSR, Entrepreneurship, Principles of Management
on Mar 15th, 2014 | 0 comments
![Code of Ethics]()
Institutionalize Your Code of Ethics Business Ethics is a term we often come across in the world of corporate business. Ethics generally distinguishes between the right and the wrong. But you might argue, what is right for one person may not be for the other. “True! But there are certain principles that are widely accepted by everyone that guides the behavior of individuals or a business enterprise. Shall we say that Business Ethics is an UNWRITTEN CODE OF CONDUCT which governs the conduct of a business enterprise and also helps it in reaching the right decision? CSR CORPORATE SOCIAL RESPONSIBILITY comes into the big picture when you talk about business or professional ethics. When a person gears up himself to start a business, he studies the market as to how supportive it would be to carry on his business. He segments the market, evaluates the demography, approaches financial institutions like banks for loans, creates a big cacophony about the government’s red tapism to acquire licenses to do his business and when all these criteria accords a green signal he ventures into the market with a confidence that is backed up by all the above factors. Say by the end of the first year, he has done great business and the time has come for income tax or sales tax payments, a small voice cuckoos from within, asking him to think twice or to venture the possibilities of EVADING TAX. Once he tastes the essence of success and the POWER OF MONEY he deviates from the RIGHT CONDUCT and BEHAVIOR. He conveniently abstains himself from performing his duties towards customers, employees, government, share holders, stake holders and others. Mind you, being ethical is a statutory phenomenon and not a thing to be taken for granted. If your motivation and effort is oriented only TOWARDS PROFIT, thriving longer in the market will become a matter of concern. Every action has an equal and opposite reaction: “Whatever is that you take, you have to repay.”This is applicable both in personal life as well in business. Yogis’ have ascertained the fact time and again that you have to dissolve your karma or past actions to be a liberated soul. Neo world scientists also second this thought,” every action has an equal and opposite reaction. “Being ethical is not that demanding or tough as you have conceived it to be. In simpler terms, it even teaches you to be highly compassionate towards your fellowmen. Various aspects affecting ethical behavior in a business organization would be: Policies regarding moral duty and obligation Accounting ethics Corporate culture Ethics in management development programmes Dealing with “gray areas” Disciplinary procedures Review and updating the ethical code Increased concern about the well informed public Government regulations Value based management practices Enlightening the managers of top cadre Rewards and recognitions for people with right conduct and the list goes on and on. Corruptions, Bribery, Black marketing are some of the JARGONS that are strictly prohibited words and actions in the dictionary of ethics. Sound ethical practices not only create an IMAGE for your company, but also the recognition among your own employees that you could relish. Being ethical is not that difficult, only that it calls for undeterred determination and inbuilt...







